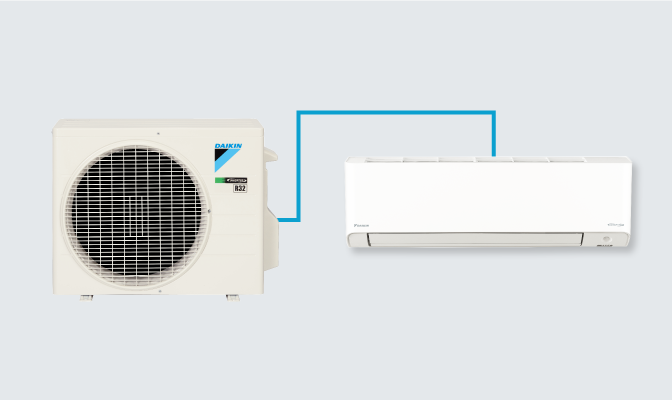
An HVAC split system refers to a type of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system commonly used in both residential and commercial buildings. The “split” in the name indicates that this system is divided into two main components, with one part located inside the building (indoor unit) and the other located outside (outdoor unit).
Here are the two main components of an HVAC split system:
1- Indoor Unit:
The indoor unit, also known as the evaporator or air handler, is typically installed inside the building, usually in a utility room, basement, attic, or a designated HVAC closet.
This unit contains the evaporator coil, which is responsible for absorbing heat from the indoor air.
The indoor unit is connected to a network of ducts that distribute the conditioned air throughout the building.
2- Outdoor Unit:
The outdoor unit, also known as the condenser, is located outside the building, often placed on a concrete pad or mounted on brackets.
This unit houses the condenser coil, a compressor, and a fan. The compressor is responsible for pressurizing and circulating the refrigerant between the indoor and outdoor units.
The fan in the outdoor unit assists in dissipating heat from the refrigerant into the outdoor air.
How an HVAC Split System Works:
1- Cooling Mode:
During the cooling mode, the indoor unit’s evaporator coil absorbs heat from the indoor air, and the refrigerant absorbs this heat, turning into a low-pressure gas.
The refrigerant is then pumped to the outdoor unit, where the compressor pressurizes it, causing it to release the absorbed heat to the outdoor air.
The refrigerant returns to the indoor unit as a low-pressure liquid, and the cycle repeats.
Heating Mode (Heat Pump Systems):
In heat pump systems, the process is reversed during the heating mode. The outdoor unit extracts heat from the outdoor air and releases it inside the building.
2- Air Distribution:
The conditioned air is distributed through the building’s ductwork by a blower in the indoor unit.
Air vents or registers in each room allow the conditioned air to enter, and return vents collect air for recirculation.
Advantages of HVAC Split Systems:
3- Flexibility: Split systems offer flexibility in terms of installation, making them suitable for a wide range of building sizes and layouts.
4- Energy Efficiency: Many split systems are designed for energy efficiency, especially those with high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) ratings.
5- Quiet Operation: The noisy components, such as the compressor and condenser fan, are located outdoors, contributing to quieter indoor operation.
6- Zoning Capability: Some split systems allow for zoning, enabling different areas of a building to be conditioned independently.
7- Ease of Maintenance: Split systems are often easier to maintain compared to other HVAC configurations.